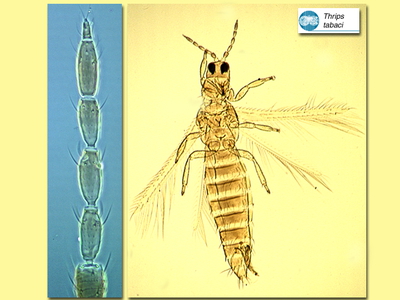
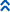
Figures
Fig. 1 Antenna and head (dorsal)
Fig. 2 Head (dorsal) and pronotum
Fig. 3 Meso- and metanotum
Fig. 4 Fore and hind wing
Fig. 5 Pleurotergite II and III
Fig. 6 Tergite VIII (female)
Species
Thrips tabaci LindemanBiology
Highly polyphagous in flowers and on leaves, the range of plants damaged includes cereal crops and lettuce plants. It is an important vector of tomato spotted wilt tospovirus, but can also be an effective predator of phytophagous mites.
Distribution
Found worldwide, but usually not in the wet tropics.
Recognition
Small to medium sized thrips, varying from yellow to brown with ocelli lacking red pigment; distal antennal segments brown, forewings pale. Antennae 7-segmented, sense cone on III & IV small and forked. Head with no setae in front of fore ocellus, one pair on anterior margins of ocellar triangle. Pronotum with 2 pairs of posteroangular setae. Metanotum with irregular reticulate sculpture medially, but a few irregular transverse lines at anterior and closely spaced longitudinal lines laterally; median setae not at anterior margin. Forewing first vein commonly with 4 setae on distal half (varying from 3 to 6). Tergite II with 3 lateral marginal setae; IV-VI with no lines of sculpture between median setae; VI-VIII with ctenidia laterally, on VIII posteromesad of spiracle; posteromarginal comb on tergite VIII complete with slender microtrichia. Sternites and pleurotergites with no discal setae, but pleurotergites with many rows of fine microtrichia.
Related species
This species is unusual in the sculpture of the pleurotergites, and apparently has no close relatives amongst the 280 members of the genus.