Figures
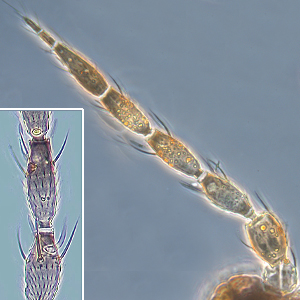
Fig. 1: Antenna (inset: III. and IV. antennal segment)
Fig. 2: Head dorsal with ocellar triangle
Fig. 3: Pronotum
Fig. 4: Meso- and metanotum
Fig. 5: Fore- and hindwing
Fig. 6: Tergites VI and VII
Fig. 7: Tergites VII and VIII
Taxonomic Information
Species:
Neohydatothrips floridanus (Watson, 1918)
Synonyms:
Sericothrips campestris Hood, 1939
Sericothrips floridanus Watson, 1918
Present taxonomic position:
Family: Thripidae Stephens, 1829
Subfamily: Sericothripinae (Karny) Priesner, 1925
Genus: Neohydatothrips John, 1929
Species Recognition
General information about the genus Neohydatothrips:There are 80 species included in this genus several have bodies that are prominently bicolored as well as banded wings while others are uniformly yellow. Characters that are common within this genus include tergites with many rows of lateral microtrichia and the forewing has a complete row of setae on the first vein whereas on the second vein there are zero or only two setae.
Typical character states of Neohydatothrips floridanus:
Body color
Mainly pale or yellow, with some darker markings or
bicolored
Antennae
Number of antennal segments: 8
Segment IV - forked sensorium: scarcely extending beyond base of segment V
Segments II and III shape: more or less symmetric
Segments III & IV sensoria: emergent and forked
Base of sensorium on antennal segment VI: no more than 2 times as wide as base of nearest seta
Terminal antennal segments: rarely elongate
Head:
Distance between bases of ocellar setae III: greater than width of first ocellus
Head shape between compound eyes: not prolonged
Postocular setae I: present
Surface of head, pronotum and fore legs: without strong reticulate sculpture
Ocellar setae I in front of anterior ocellus: present
Prothorax
Number of pairs of elongate pronotal setae: 0-3
Number of pairs of elongate posteroangular pronotal setae: 1
Pronotum shape: rectangular
Sculptur of pronotum: with transverse striate sculpture
Length of anteromarginal median seta: S1 longer than S2
Mesothorax
Mesothoracic endofurca: with median spinula
Metathorax
Metanotal median area sculptured lines: transverse
at anterior, but longitudinal and parallel on posterior half
Metanotal median
setae length: longer than lateral metanotal setae
Metanotal median setae
position: arising at anterior margin
Metanotum: with campaniform sensilla
Metanotum major sclerite: with two major sclerites, metascutum and metascutellum
Metanotum median area: with no equiangular reticulation
Metanotum sculpture: without dominant sculptured triangle medially
Metathoracic endofurca: transverse, sometimes with simple median spinula
Wings
Wings: present and more than half as long as abdomen
First vein of forewing: distinct from costal vein
Forewing anterior margin: with setae and cilia but cilia longer than setae
Forewing color: alternating bands of dark and light
Forewing costal fringe of cilia: arising at anterior margin of wing
Forewing costal setae at middle of wing: longer or shorter than median width of wing
Forewing first vein setal row: complete, with setae closely and uniformly spaced
Forewing posterior margin cilia: undulated near apex
Forewing second vein setal row: incomplete, with setae not closely and
uniformly spaced or with no setae
Forewing surface: not reticulate Forewings:
with veins, setae and microtrichia
Legs
Fore tibial apex: not extending around fore tarsus
Mid and hind tarsi: with two segments
Abdomen:
Abdominal segment X: never tubular, longitudinally incomplete ventrally in both sexes
Abdominal sternite III of female: without glandular areas
Abdominal sternite VII: with marginal setae but no discal setae
Abdominal sternite VII median marginal setae: arising in front of margin
Abdominal sternites IV , V and VI: with marginal setae but no discal setae
Abdominal sternites V & VI microtrichia: extending fully across discal area
Abdominal tergites: without curved wing-retaining setae
Abdominal tergites IV & V median setal pair: longer than distance between their bases
Abdominal tergites V-VII: without paired ctenidia, sometimes with irregular microtrichia
Markings on tergites IV to VI: with shaded areas laterally and antecostal ridges dark
Setae on abdominal tergite X: slender
Surface of lateral thirds of abdominal tergites: with many regular rows of fine microtrichia
Ctenidia on tergite VIII: not present, but groups of microtrichia
Tergite VIII posteromarginal comb of microtrichia: present, complete medially
Tergite VIII posteromarginal microtrichia: long, slender and regular
Biology
Life history:
As with other thrips species the life cycle from egg to adult is dependent on temperature. The full cycle can take about 15 days (Lewis,
1973) to over a month and adults may live for more than one month producing several generations in one year depending on seasonal weather. With greenhouse temperatures the developmental time from egg to adult can decrease to about one week.
Host plants:
Ambrosia or ragweed (Compositae)
Vector capacity:
None identified
Current known distribution:
Africa, Asia, Australia, New Zealand,
Central and South America, Europe, North America
Additional notes:
Neohydatothrips
floridanus is found breeding in Ambrosia (ragweed) in Florida
and when populations build to high numbers this species can be found on
other plant species.
Bibliography
Childers, CC & Nakahara, S (2006): Thysanoptera (thrips) within citrus orchards in Florida: Species distribution,
relative and seasonal abundance within trees, and species on vines and
ground cover plants. - Journal of Insect Science 6.
Lewis, T (1973): Thrips their biology,
ecology and economic importance. Academic Press Inc., London Ltd. 349
pp.
Moritz G, Morris DC, Mound LA (2001): ThripsID -
Pest thrips of the world. ACIAR
and CSIRO Publishing Collingwood, Victoria, Australia, CDROM ISBN
1 86320 296 X.
Moritz G, Mound LA, Morris DC, Goldarazena A (2004): Pest
thrips of the world - an identification and information system using molecular
and microscopial methods. CBIT, University of Queensland,CDROM ISBN 1-86499-781-8.
Mound, LA & Kibby, G (1998): Thysanoptera: An identification
guide, (2nd edition). CAB International, Wallingford and New York,
70pp.
Mound, LA & Marullo, R (1996): The
thrips of Central and South America: An Introduction (Insecta: Thysanoptera).
Associated Publishers, Gainesville.
Nakahara S (1988): Generic assignments of North American species
currently assigned to the genus Sericothrips Haliday (Thysanoptera:
Thripidae). Proceedings of the Entomological Society of Washington 90: 480–483.
Links:
Mound, LA (2005): Thysanoptera (Thrips) of the World
- A Checklist. http://www.ento.csiro.au/thysanoptera/worldthrips.html